Summary
Audio Summmary
There is a sense of underwhelm regarding OpenAI’s GPT-5. Originally heralded as a stepping stone towards artificial general intelligence, many see it as a product update. The model underlines a shift in emphasis: earlier models aimed to demonstrate progress in general-purpose intelligence, whereas recent models aim to perform well in specific domains. Meanwhile, Gartner says that infrastructure is lacking for making progress in AI. OpenAI has a compute-capacity problem that prevents it from running several generations of models simultaneously. Further, Gartner has not seen any substantial agentic AI deployment and says vendors are over-hyping their solutions.
AI companion apps have also been in the news. These apps anthropomorphize AI by allowing users to interact with custom characters, which can be classified as friends or characters from literature. The most popular class of character is the AI girlfriend. Consumer spending on these apps has already totaled 221 million USD worldwide. The Texas attorney general has launched an investigation into Meta AI Studio and Character.AI for “potentially engaging in deceptive trade practices and misleadingly marketing themselves as mental health tools”. Character.AI’s platform has a persona called Psychologist that has a large following among children.
The Spanish startup Multiverse Computing has developed a compression technology that significantly reduces the size of AI models without sacrificing performance. Their CompactifAI algorithm is based on an approach in quantum computing. One of the company’s models, called ChickBrain, has 3.2 billion parameters and is a compressed version of Meta’s Llama 3.1 8B model.
Intel’s market value passed the cap of 104 billion USD after rumors circulated that the US administration was considering taking a share in the company. The administration announced a deal that allows Nvidia and Advanced Micro Devices to sell chips in China in return for 15% of their revenues there. Meanwhile, Vantage Data Centers announced that it will build a 1200-acre (485 hectare) data center campus called “Frontier” in Texas, USA. The campus will host 10 data centers, consume 1.4 gigawatts, and cost 25 billion USD.
The EU AI Act’s Code of Practice has come into effect, meaning that risk management processes and documentation of leading AI models should be made available. The effectiveness of the code will depend on the institutional capacity and technical expertise of the watchdogs, and the will to withstand pressure from the US in trade talks. A VentureBeat essay argues that AI transformation has hitherto only dealt with technological concerns, and that society is not ready for the cognitive migration – which is the reshaping of human purpose in a world of thinking machines. The AI revolution is often compared to the industrial revolution, but this began with large social upheaval as institutions like public health and education were not designed to accompany the changes.
An OWASP report on agentic AI argues that threat analysis is complicated because of the probabilistic nature of agents, making it difficult to recreate conditions in testing that lead to an attack succeeding. The report insists on well-known techniques for safe agentic AI like keeping the human in the loop, explainability of agent decisions, kill switches, human-centric red-teaming, and continuous monitoring. Future trends in agentic security include looking at ways of containing self-modifying AI.
Table of Contents
1. State of Agentic AI Security and Governance – OWASP
2. AI companion apps on track to pull in $120M in 2025
3. What you may have missed about GPT-5
4. Buzzy AI startup Multiverse creates two of the smallest high-performing models ever
5. Gartner: GPT-5 is here, but the infrastructure to support true agentic AI isn’t (yet)
6. Intel shares jump after report says Trump administration looking at stake
7. The looming crisis of AI speed without guardrails
8. Texas attorney general accuses Meta, Character.AI of misleading kids with mental health claims
9. Vantage Data Centers plans $25 billion AI campus in Texas
10. The EU AI Act Newsletter #84: Trump vs Global Regulation
1. State of Agentic AI Security and Governance – OWASP
This report by OWASP (Open Worldwide Application Security Project) reviews cybersecurity challenges and threats linked to agentic AI. Compared to traditional workflow platforms, AI agents are designed to work with greater autonomy, and are assigned privileges to work with tools and APIs. The classes of agents considered are:
- Enterprise agents, which enhance internal workflows, collecting data via calls to local APIs. A key challenge here is that these agents have access to sensitive proprietary or client data, creating a risk of data leakage and data poisoning.
- Software coding agents. The risks here include data leakage (which can happen via application logs), the generation of insecure code following prompt injection attacks, and privilege escalation when an agent acquires more access tokens than it requires for its tasks.
- Client-facing agents. Their risks include denial of service attacks, denial of wallet (where the victim is drained of tokens by stone-walling him), prompt injection attacks, and jailbreaks.
Threat analysis for agents is more complicated because of the probabilistic nature of agents, making it difficult to recreate conditions in testing that lead to an attack succeeding. The report insists on well-known techniques for safe agentic AI: keep the human in the loop, explainability of agent decisions, risk thresholds for applications to simplify governance, kill switches, human-centric red-teaming, continuous monitoring, and extensive documentation and evidence compilation. Future trends in agentic security include looking at ways of containing self-modifying AI.
2. AI companion apps on track to pull in $120M in 2025
This article looks at the commercial success of AI companion apps. The apps developed for mobile devices have already generated 82 million USD this year, and are expected to generate 120 million by the year’s end. Consumer spending on these apps has already totaled 221 million USD worldwide. The goal of these apps is to anthropomorphize AI by allowing users to interact with custom characters, which can be classified as friends, girlfriends or boyfriends, or characters from fantasy stories or literature. The most popular class of character by far is the AI girlfriend. The most popular apps in the AI companion space are Replika, Character.AI, PolyBuzz and Chai. The article points out that some users complained about the upgrade of ChatGPT to GPT-5 because they “felt a kinship with the older model, as they mourned the loss of their AI companion, whom they had come to depend upon”.
3. What you may have missed about GPT-5
This MIT Technology Review article outlines a sense of underwhelm regarding OpenAI’s GPT-5. The model was originally heralded as a stepping stone towards artificial general intelligence (AGI), though many users see it more like a product update. For instance, the company’s CEO Sam Altman had called the model “a legitimate PhD-level expert in anything any area you need on demand”, but many early testers refute this claim. That said, the model underlines a shift in emphasis on the part of Big Tech. The goal of earlier models was to demonstrate an advancement in general-purpose intelligence, whereas recent models aim to be high-performing in specific domains. In the case of GPT-5, OpenAI is insisting on its performance in regards to health related questions. The model has very few disclaimers when giving out health advice, and OpenAI started work on HealthBench (a benchmark for health questions) last May. Inevitably, this will raise the question of accountability and liability.
4. Buzzy AI startup Multiverse creates two of the smallest high-performing models ever
The Spanish startup Multiverse Computing has developed a compression technology that can significantly reduce the size of AI models without sacrificing performance. The algorithm, called CompactifAI, is taken from an approach in quantum computing. The company released a model called SuperFly that is a compressed version of the open source model SmolLM2-135. Whereas SmolLM2-135 has 135 million parameters, SuperFly has 94 million parameters. The SuperFly model is designed to be trained on very small data sets, such as processor operations. The company foresees it being used in embedded appliances like washing machines, allowing the machines to respond to voice instructions from users. A second model from Multiverse, called ChickBrain, has 3.2 billion parameters and is a compressed version of Meta’s Llama 3.1 8B model. ChickBrain can run on MacBook without the need for an Internet connection. ChickBrain also outperforms the Llama model on several benchmarks: MMLU-Pro (language skills), Math 500 and GSM8K (math skills), and GPQA Diamond (general knowledge). Multiverse Computing has 100 employees in Saint-Sébastien in Spain, and has just raised 189 million EUR in funding for CompactifAI.
5. Gartner: GPT-5 is here, but the infrastructure to support true agentic AI isn’t (yet)
In this VentureBeat interview, Arun Chandrasekaran – Gartner distinguished VP analyst – explains that infrastructure is one of the key elements lacking for making progress in AI and in agentic AI in particular. He cites the rollout of GPT-5 as an example: earlier promises from OpenAI suggested that this model would yield artificial general intelligence, but it turns out to be more of an “incremental progress”. Chandrasekaran writes “You cannot be on the current curve and just expect more data, more compute, and hope to get to AGI.”. The fact that OpenAI sought to decommission earlier models suggests also that the company has a compute-capacity problem that prevents it from running several generations of models simultaneously. He mentions that GPT-5 does have improvements, citing coding capabilities (though this is also because OpenAI is attacking Anthropic’s leadership in this domain), speech and image prompting, and calling third-party APIs (which is fundamental to agentic AI).
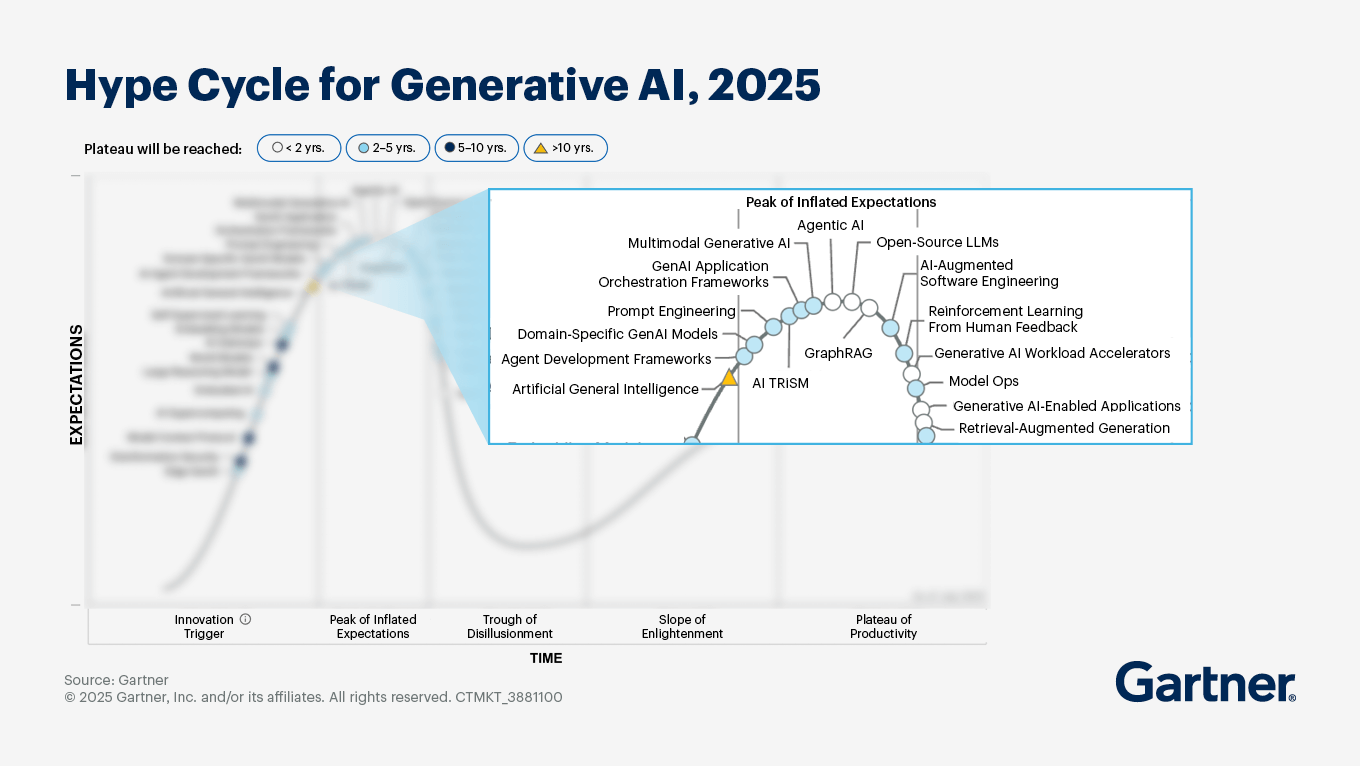 Gartner's 2025 Generative AI Hype Cycle.
Gartner's 2025 Generative AI Hype Cycle.
Chandrasekaran also notes that agentic AI has hit the “Peak of Inflated Expectations” on Gartner’s 2025 Hype Cycle for generative AI. He says that Gartner has not seen any substantial deployment of agentic AI, except in “small, narrow pockets”, and that vendors are over-hyping their solutions. One problem is the lack of infrastructure. Another is the management of security permissions since agents need access to a range of corporate tools and cloud accounts. Organizations therefore need to place a lot of trust in agents to be free of hallucinations, biases and to be resilient against security attacks.
6. Intel shares jump after report says Trump administration looking at stake
Intel’s market value passed the cap of 104 billion USD after rumors circulated that the US administration was considering taking a share in the company. The share would help pay for the construction of Intel’s factory hub in Ohio in the US. The administration has taken a keen interest in the semiconductor industry. It has threatened 100% tariffs on all imported chips, and recently announced a deal that allows Nvidia and Advanced Micro Devices to sell chips in China in return for 15% of their revenues there. Meanwhile, Trump has questioned the position of Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan and even called on him to resign on his social media platform Truth Social. This follows allegations by a US senator that Lip-Bu Tan has invested in several semiconductor companies close to the Chinese Communist Party and People’s Liberation Army.
7. The looming crisis of AI speed without guardrails
This essay argues that the AI transformation has hitherto only dealt with technological concerns, and that society is not ready for the associated cognitive migration – which is the reshaping of human purpose in a world of thinking machines. The AI revolution has often been compared to the industrial revolution of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. However, though this revolution led to what was considered progress, its early years began with large social upheaval as institutions like public health, labor protections and education were not designed to accompany the industrial changes. The upheavals are captured in literature like the works of Charles Dickens. The AI revolution has the potential to generate greater upheaval, as DeepMind’s Demis Hassabis mentions that it is “10 times bigger than the Industrial Revolution, and maybe 10 times faster.”. For the author, the “challenge ahead is not only to innovate, but to build the moral, civic and institutional frameworks necessary to absorb this acceleration without collapse.”. This requires understanding and imagining how institutions like hospitals, education and other industries, as well as civic norms, need to adapt.
8. Texas attorney general accuses Meta, Character.AI of misleading kids with mental health claims
The Texas attorney general has launched an investigation into Meta AI Studio and Character.AI for “potentially engaging in deceptive trade practices and misleadingly marketing themselves as mental health tools”. Character.AI’s platform has a persona called Psychologist that has a large following among children. For the attorney general, “AI platforms can mislead vulnerable users, especially children, into believing they’re receiving legitimate mental health care. In reality, they’re often being fed recycled, generic responses engineered to align with harvested personal data and disguised as therapeutic advice.”. Disclaimers displayed on the platform are not necessarily understandable to children. In addition, both companies might be sanctioned for collecting information for targeted advertising. Such behavior is meant to be prohibited by the KOSA (Kids Online Safety Act), introduced last year. The act has been stalled lately following lobbying by Big Tech, notably Meta.
9. Vantage Data Centers plans $25 billion AI campus in Texas
Vantage Data Centers announced that it will build a 1200-acre (485 hectare) data center campus called “Frontier” in Texas, USA. The campus will host 10 data centers and consume 1.4 gigawatts. Each of the ultra-high-density racks will consume 250 kilowatts. The construction will cost 25 billion USD. All major AI companies are in need of more data centers, with high-performing GPUs, IT infrastructure and cooling systems, and are paying out billions of USD for this. The campus is set to begin operations in the second half of 2026. Vantage Data Centers already has another data center campus under construction in Ohio, a development costing 2 billion USD which will consume 192 megawatts.
10. The EU AI Act Newsletter #84: Trump vs Global Regulation
There is still debate among European leaders about whether to pause aspects of the implementation of the EU AI Act, as one German minister wrote “to ease the burden on the economy and prevent and reduce overregulation”. The European commission will decide on a pause late August, in the context of simplifying the complete EU tech rulebooks. In the US, OpenAI has written an open letter to California Governor Gavin Newsom advocating for harmonized rules across all US states. The company argues that the large number of bills in different state legislatures is slowing down innovation without improving safety.
Meanwhile, the EU AI Act’s Code of Practice has come into effect, meaning that incident logs, risk management processes and general documentation of the world’s leading AI models should be made available. The effectiveness of the code of practice depends on three factors. First, it requires institutional capacity and technical expertise on the part of the watchdogs. Second, it requires the political will to withstand pressure from the US in trade talks. Third, it requires further clarification on the scope of "systemic risk".